Ryne C. Allen
Desco Industries Inc. (DII), Employee Owned
November 1999
Reproduced with Permission, EE-Evaluation Engineering, November,
1999
I. Introduction to ESD
Control Programs
ESD Control programs are an essential part of a quality process and
are always needed when handling ESD sensitive electronic/semiconductor devices. The extent
of the ESD Control program is determined by the ESD Sensitive (ESDS) devices themselves
and how they are handled. Refer to article "How to Set Up an ESD Control
Program" [1] for additional information.
One of the main reasons that companies deploy ESD Control programs
is to save money. Increased throughput and decreased scrap can yield a Return On
Investment (ROI ) of up to 1,000% per [2]. A secondary reason is to comply with their
customers’ and ISO 9000 type programs’ requirements. Whatever reason, setting up
and implementing an ESD Control program will almost always produce favorable financial
results.
II. Cost Reduction via ESD Control Programs
Having ESD awareness and following through with an ESD Control
program is essential in reducing quality failures due to ESD. ESD can affect product
reliability with catastrophic damage which is readily apparent to latent degradation.
Latent degradation is particularly expensive requiring costly inspection and rework cycles
in-house or product failure in the field. Maintaining good ESD controls will improve
product throughput or yield, increasing reliability in the field which improves customer
satisfaction leading to increased future business.
One test equipment manufacturer noted that GMR
heads were being damaged during or after testing. These heads are extremely sensitive to
ESD, and require additional handling precautions.
It is very important when designing and implementing an ESD Control
program to know the ESD susceptibility of the ESD Sensitive (ESDS) devices you are trying
to protect. Classification of these devices should include all simulation models human
body model (HBM), Machine Mode (MM), and Charged-device Model (CDM) that will properly
characterize the devices' sensitivity when handled at various locations within the
facility [6]. This will allow for the most economical program design.
Gene Chase, an ESD Consultant with ETS Inc., is quoted as saying
"Millions of dollars are lost every year due to ESD [4]. Many of these incidents
occur within the computer and communications industry." Examples of losses from ESD
may be any of the following:
- Lost Time
- Loss of Connection
- Loss of Data
- Shocks to Personnel
- Upset to A System Requiring A Re-Boot
- Damage to Equipment
- Equipment Hardware Failure
To properly determine the return on investment (ROI) from your ESD
Control program, you must collect return, repair and scrap cost data before and after
implementation.
Terry O’Malley, former AT&T ESD Manager, had collected data
from several AT&T facilities both before and after instituting an ESD Control program.
The data speaks for itself; see figure 1 for a graph of two facilities that were
monitored. There was over a 50% savings in return and repair costs found at both
facilities after initiating their ESD Control programs.
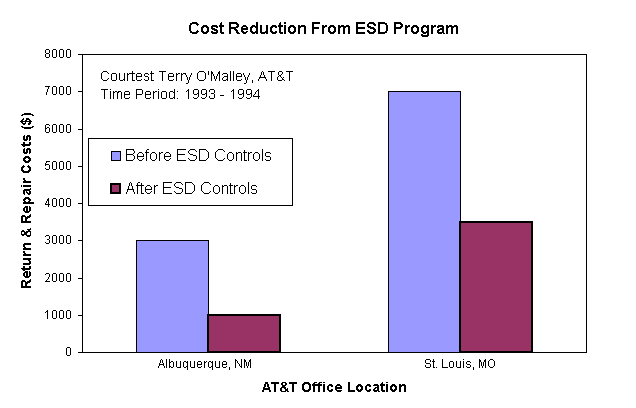
Figure 1 – Cost Reduction From ESD Program,
AT&T Office Location
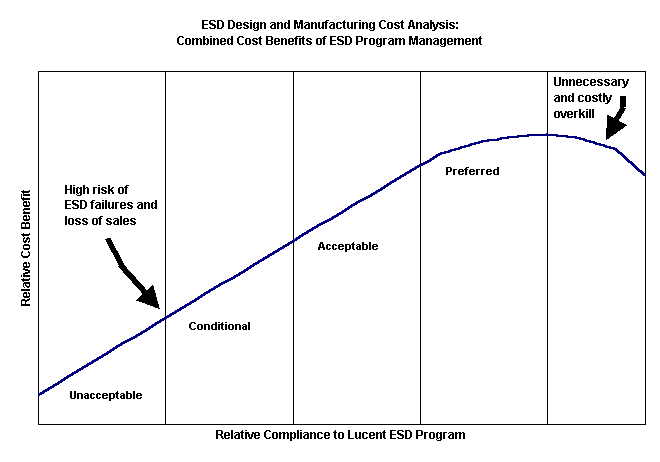
Figure 2 - ESD Design and Manufacturing Cost
Analysis:
Combined Cost Benefits of ESD Program Management [2]
Figure 2 abstractly represents the relative cost benefits of
Lucent’s ESD Control program with the relative compliance to this program [2]. A
typical return on investment (ROI) for a strict ESD Control program, like that used at
Lucent Technologies, is typically 1,000 %. The design of the ESD Control program should be
well thought out to minimize unnecessary costs in the program, but with this knowledge,
major quality and reliability failures have been known to cost up to $10 million dollars
each and jeopardize sales.
Protecting an ESDS device at all but one of the workstations is not acceptable. For the
ESD Control program to be effective, it must be comprehensive and followed with discipline
throughout the manufacturing, transport, and storage cycle. Management commitment is an
important element of any effective ESD Control Program. ESD damage is not simple or
inexpensive to identify. To improve quality and profits, management should be involved.
Over 21% of failure analysis is due to electronics and industry studies showing that 30%
of all electronic failures can be attributed to ESD.
Major companies including AT&T, Motorola, Hewlett Packard and IBM have been able to
successfully track ESD damage cost and the resulting benefits of their ESD Control
Programs. These companies have determined that ESD Control is an essential part of their
success, one that results in significant investment pay-back, refer to Figure 1.
Even with an ESD Control program in place, a typical electronics company may lose 5% of
revenue from all causes of product failure. Cost avoidance is the biggest issue when it
comes to implementing an ESD Control program. Another source [5] states that a typical
pay-back on an ESD control program is 95:1. For every one-dollar invested in ESD control,
ninety-five dollars comes back as money saved [5].
V Increased Sensitivity to ESD Control and some causes
Difference in component sensitivity between through-hole and surface
mount devices is dependent on the architecture and technology packaged. Typically, surface
mount devices have much smaller architecture making them more susceptible to ESD than
through-hole packaged devices. The width of the circuitry conductors is as small as 0.10
micrometer (equal to 0.0001millimeter or 0.000004 inch). To pack more and more circuitry
into small packages, the spacing isolating circuitry has been reduced and can be as little
as 300 m m. A human being cannot feel ESD voltage until it reaches approximately 3,000
volts. A discharge of static electricity is literally a little lighting bolt, producing
heat that can easily burn through microelectronic architecture some rated with a withstand
voltage as low as volts.
Technology
Trends |
| Year |
1995 |
1998 |
2001 |
2004 |
2007 |
| Feature size (mm) |
0.35 |
0.25 |
0.18 |
0.12 |
0.10 |
| Voltage (V) |
3.5 |
2 - 3.5 |
1.50 – 1.9 |
1.0 – 1.5 |
1.0 |
Source: Terry Welsher, Bell Labs, Lucent Technologies, 12/2/97 [5]
Table I – Feature size and device power trends
For IC packaging, the Input/Output (I/O) count has climbed
from 600 to 1,000 to well over this now. This implies that the spacing between the I/Os
have decreased dramatically and where wire bonding is used, the air gap becomes that much
smaller making the neighboring I/Os even more susceptible to ESD. This can be seen as Ball
Grid Array (BGA) chips have been replacing through-hole pin chip technology
The increasing sophistication of electronic devices has continued to make electronic
devices more and more susceptible to ESD related damage. This is a trend that is expected
to continue.
Dry areas further add to the susceptibility of ESD Sensitive (ESDS) devices. Table II
shows normal activity within a production facility where turboelectric charging levels of
operators and objects are given in voltages and shown to be dependent on relative humidity
(RH). There can be over a 5 time increase in charge generation when the RH drops to 10%.
Table II
TYPICAL ELECTROSTATIC VOLTAGES* |
EVENT |
RELATIVE
HUMIDITY |
10% |
40% |
55% |
| Walking across carpet |
35,000 |
15,000 |
7,500 |
| Walking across vinyl floor |
12,000 |
5,000 |
3,000 |
| Motions of bench worker |
6,000 |
800 |
400 |
| Remove DIPs from plastic tubes |
2,000 |
700 |
400 |
| Remove DIPs from vinyl trays |
11,500 |
4,000 |
2,000 |
| Remove DIPs from Styrofoam |
14,500 |
5,000 |
3,500 |
| Remove bubble pack from PCBs |
26,000 |
20,000 |
7,000 |
| Pack PCBs in foam-lined box |
21,000 |
11,000 |
5,500 |
|
*Source: AT&T ESD Control Handbook-1989
|
There are a slew of other factors that can add to the problems
that need to be countered by a well designed ESD Control program, such as: employee
knowledge with training; ESD Control products designed to protect the corresponding ESDS
devices; program funding with management buy-in; employee compliance with internal
discipline and audits, etc.
Conclusion:
A properly designed and successfully deployed ESD Control program is
a proven money saver with an ROI of up to 1,000% per year. Another source reports that for
every one-dollar invested in ESD control, ninety-five dollars comes back as money saved.
Have you hugged your ESD Coordinator recently?
REFERENCES
- "How to Set UP and ESD Control Program", Allen, Ryne, EE,
February 1999
- ESD Program Management, 2nd Edition, Dangelmayer, G.
Theodore, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, MA, 1999
- Electrostatic Discharge Control, McAteer, Owen J., McGraw Hill
Publishing, New York, 1990
- Chase, Gene, Gene Chase's Shocking Home Page, 6/99
- ESD Association, NE Chapter General Meeting, Speaker: Terry Welsher,
Bell Labs, Lucent Technologies, 12/2/97
- The ESD Association, 7900 Turin Road, Bldg. 3, Suite 2, Rome, NY
13440-2069, http://esda.org
About the Author
Ryne C. Allen graduated from Northeastern University with B.S.E.E,
M.S.E.E., and MBA degrees. Prior to joining Desco Industries Inc. was chief engineer and
lab manager at the Plasma Science and Microelectronics Research Laboratory at Northeastern
University. Mr. Allen is a NARTE-certified ESD control engineer and the author of 27
published papers and articles. He is a member of the ESD Association and an active ADCOM
member of the local Northeast Chapter of the ESD Association.